math4610
USU Math 4610
Contents Number Test Software Manual
Name: Condition Number Test
Author: Philip Nelson
Language: C++. The code can be compiled using the GNU C++ compiler (gcc). A make file is included to compile an example program
For example,
make
will produce an executable ./conditionTest.out that can be executed.
Description/Purpose: The purpose of this code is to test the performance of the parallel vs serial algorithm to compute the condition number of a matrix, A.
Usage/Example:
int main()
{
for (auto i = 40u; i <= 640u; i *= 2)
{
auto A = generate_square_symmetric_diagonally_dominant_matrix(i);
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto conditionNum1 = condition_2_estimate(A, 50u);
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto result1 =
std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(end - start).count();
start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto conditionNum2 = parallel_condition_2_estimate(A, 50u);
end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto result2 =
std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(end - start).count();
std::cout << i << " x " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "serial algorithm:\n result: " << conditionNum1
<< "\n time: " << result1 << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "parallel algorithm:\n result: " << conditionNum2
<< "\n time: " << result2 << std::endl
<< std::endl;
}
}
Output from the lines above
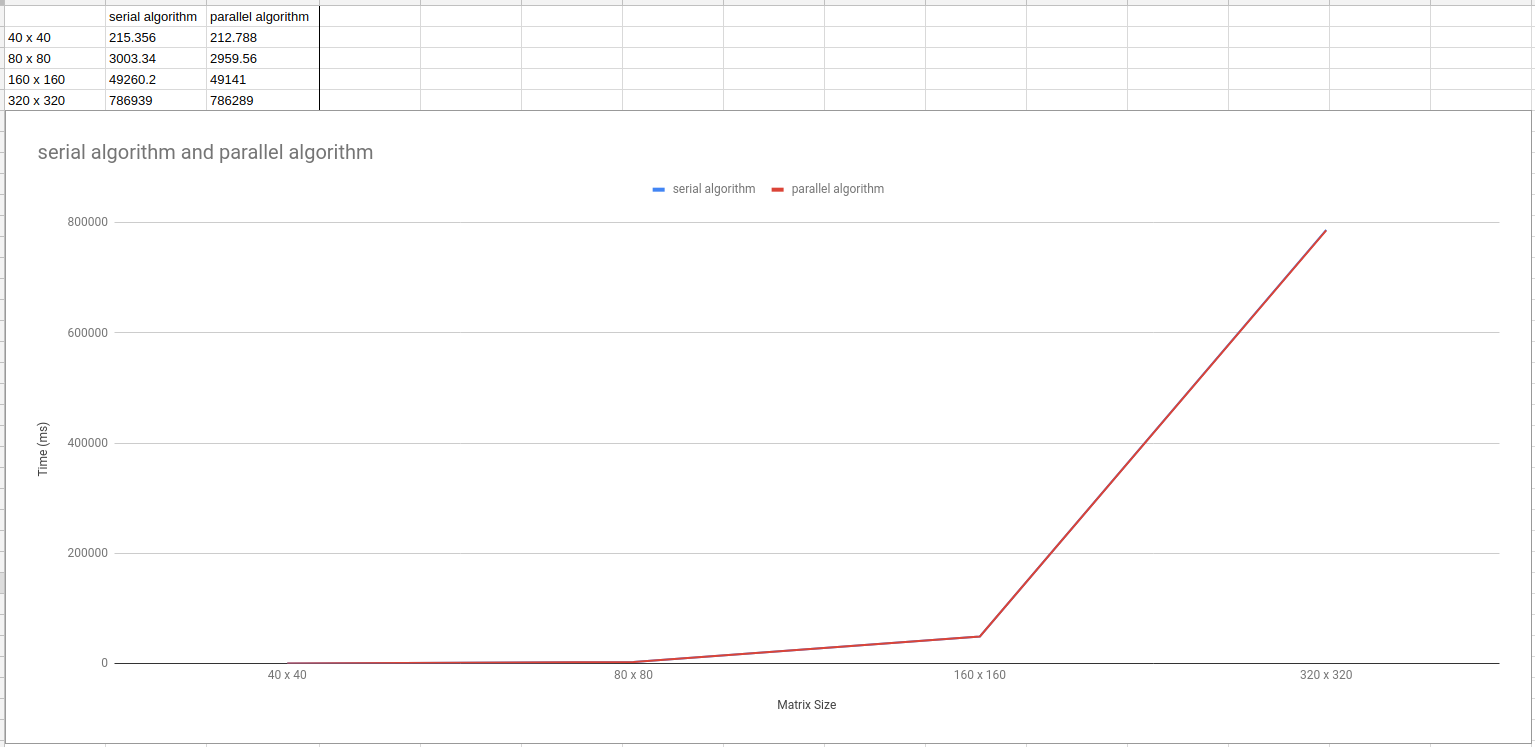
explanation of output:
The results were not greatly in favor of the parallel algorithm. Both algorithms performed similarly with the parallel version outperforming the serial version by a small margin. The graph shows how the time increases exponentially as is to be expected. The marginal performance grain is not to be expected. Something is likely incorrect.
Last Modified: December 2018