math4610
USU Math 4610
Parallel Matrix Vector Multiply
Author: Philip Nelson
Language: C++. The code can be compiled using the GNU C++ compiler (gcc)
Description/Purpose: This page demonstrates the utility of OpenMP in parallelization.
Findings
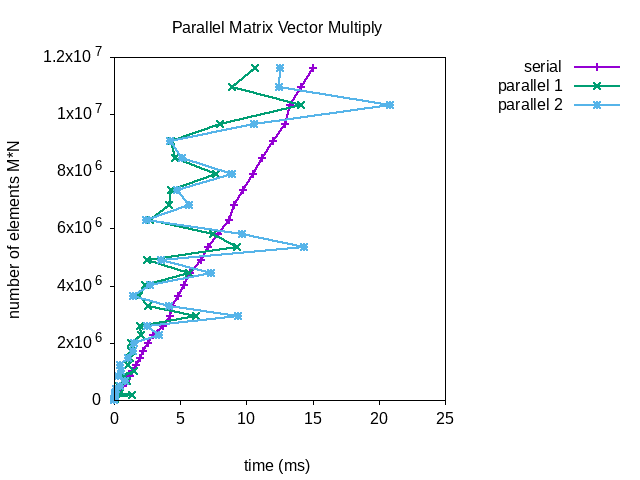
These results are impressive overall but there are some anomalies. I don’t know why it takes the parallel functions longer sometimes. We can see that both parallel methods outperform the serial version. With the largest matrices the first parallel function outperforms the second.
Implementation/Code: The following is the code for parallel_multiply
Two versions were tested. Version one used #pragma omp for to parallelize the outer for loop. Version 2 used #pragma omp for collapse(2) to parallelize the outer and inner loops.
template <typename T>
using Matrix = std::vector<std::vector<T>>;
template <typename T, typename U, typename R = decltype(T() + U())>
std::vector<R> parallel_multiply(Matrix<T> const& m, std::vector<U> const& v)
{
if (m[0].size() != v.size())
{
std::cerr
<< "ERROR: incorrectly sized matrix or vector in parallel mat * vec\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
std::vector<R> result(m.size(), 0);
auto i = 0u, j = 0u;
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (i = 0u; i < m.size(); ++i)
{
for (j = 0u; j < m[0].size(); ++j)
{
result[i] += m[i][j] * v[j];
}
}
}
return result;
}
template <typename T, typename U, typename R = decltype(T() + U())>
std::vector<R> parallel_multiply2(Matrix<T> const& m, std::vector<U> const& v)
{
if (m[0].size() != v.size())
{
std::cerr
<< "ERROR: incorrectly sized matrix or vector in parallel mat * vec\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
std::vector<R> result(m.size(), 0);
auto i = 0u, j = 0u;
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for collapse(2)
for (i = 0u; i < m.size(); ++i)
{
for (j = 0u; j < m[0].size(); ++j)
{
result[i] += m[i][j] * v[j];
}
}
}
return result;
}
Last Modified: October 2018